Various Anderson-type polyoxometalate-based metal–organic complexes induced by diverse solvents: assembly, structures and selective adsorption for organic dyes†
Abstract
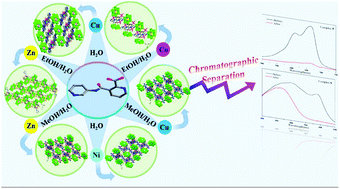
Six new Anderson-type polyoxometalate (POM)-based metal–organic complexes (MOCs), namely, {HCu(HPCAP)2[CrMo6(OH)6O18]}·2H2O (1), {Zn4(PCAP)2[CrMo6(OH)6O18]2(H2O)12}·4H2O (2), {Zn3(PCAP)2[CrMo6(OH)5O19](H2O)6}·6H2O (3), {Ni3(PCAP)2[NiMo6(OH)5O19](H2O)6}·8H2O (4), {Cu3(PCAP)2[AlMo6(OH)5O19](H2O)6}·6H2O (5), and {Co3(HPCAP)2[AlMo6(OH)6O18](H2O)10}[AlMo6(OH)6O18]·6H2O (6) (HPCAP = 3-(2-pyridinecarboxylic acid amido)pyridine), were constructed from diverse metal ions (CuII/ZnII/NiII/CoII), the HPCAP ligand and various Anderson-type POM anions under hydrothermal and solvothermal conditions and structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, IR spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and thermogravimetric analyses (TGA). Crystal analysis shows that complex 1 has a 3D supramolecular structure based on the CrMo6 anions and the 1D metal–organic ribbon chains [Cu(HPCAP)2] via hydrogen bonds. Complex 2 is a 2D supramolecular layer composed of two kinds of dinuclear metal clusters of [Zn2(CrMo6)2] and [Zn2(PCAP)2]. Complexes 3–5 show similar 3D frameworks. In 3–5, [M1Mo6]3− (M1 = Cr for 3, Ni for 4, and Al for 5) anions are bridged by MII ions (M = Zn for 3, Ni for 4, and Cu for 5) to give a 1D M–M1Mo6 inorganic chain; the adjacent 1D inorganic chains are connected through two directions of [M2(PACP)2] rings to form a 3D framework. It should be noted that in complex 4, the NiMo6 anions are in situ generated from the NiII ion and Mo7O246− anions, which is rarely observed in POM-based MOCs. Complex 6 shows a 1D ladder-like supramolecular double chain, which is composed of 1D Co–AlMo6 inorganic chains, [Co2(HPCAP)2] dual-core rings and discrete AlMo6 polyanions interlinked by hydrogen bonding interactions. These structural diversities show that solvents play key roles in the construction of various architectures. All of the title complexes have excellent adsorption activities for the cationic dyes methylene blue (MB) and gentian violet (GV); in particular, complex 5 is capable of selectively adsorbing MB and GV from the mixtures of MB and MO and GV and MO, respectively. In addition, the electrochemical properties of complexes 1, 4, and 5 are also studied.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...