Fluorescence spectroscopy studies of crossed aldol reactions: a reactive Nile red dye reveals catalyst-dependent product formation†
Abstract
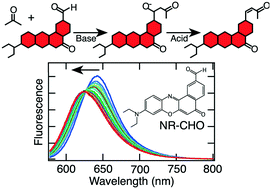
The synthesis of a new Nile red derivative incorporating a reactive aldehyde moiety (NR-CHO) is reported and its use in spectroscopic studies of heterogeneous catalyst activity in crossed aldol reactions is demonstrated. 1H and 13C NMR, and high-resolution mass spectrometry confirmed the desired NR-CHO was obtained. Mg-Zr-Cs doped silica (Cs(Zr,Mg)-SiO2) was employed as the catalyst and its performance was compared to that of commercially available MgO. Fumed silica was used as a control. Aldol reactions with acetone and acetophenone were run in 4 : 1 (v/v) DMSO : ketone solutions in the presence of both dilute (1 μM) and concentrated (1 mM) NR-CHO. NR-CHO fluorescence spectra were acquired as the reactions progressed. Shifts in its emission spectrum are used to distinguish the products formed and to characterize the reaction rate. The dye exhibits different behavior that defines whether the reaction stops at the addition (alcohol) product, or forms both addition and condensation (olefin) products, providing valuable initial information on catalyst activity. The assignment of addition and condensation products is supported by thin layer chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and HPLC-mass spectrometry data. Product formation is shown to depend upon the catalyst employed, with the Cs(Zr,Mg)-SiO2 yielding both addition and condensation products, while MgO yields primarily addition products. The advantages of NR-CHO in spectroscopic studies of aldol reactions are also demonstrated relative to commercially available 3-perylenecarboxaldehyde. The NR-CHO reported here and the results obtained will facilitate a broad range of both ensemble and single molecule spectroscopic investigations of heterogeneous catalysis in crossed aldol reactions in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...