Sol–gel synthesis of large-sized polycrystalline stannous oxide and its oxidation behavior†
Abstract
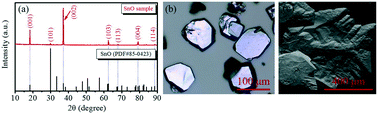
The large-sized polycrystalline stannous oxide (SnO) synthesized by a sol–gel method was found to have attractive crystal structural properties and thermo-oxidative stability. The present work describes the thermal stability performance of this large-size polycrystalline material at different temperatures in air. The obtained results showed a systematic oxidation from SnO to stannic oxide (SnO2) in the range of 450–1300 °C and SnO completely oxidized to SnO2 above 900 °C, but it was in a stable state under 450 °C. Other than this, the lattice parameters of SnO and SnO2 also changed slightly at different temperatures. For instance, the lattice parameters of SnO changed from a = b = 3.799 nm and c = 4.841 nm (at room temperature (RT)) to a = b = 3.803 nm and c = 4.838 nm at 300 °C, and the lattice parameters of SnO2 also changed at 600 °C, 700 °C, and 1000 °C. In addition, the present work also explored the effect of oxygen on the crystal surface at RT. The obtained results showed a slow oxidation process from SnO to SnO2 by being in contact with oxygen. Only 6.4% of SnO on the crystal surface was oxidized after one week, which indicated that SnO was a steady-state material. The obtained large-sized polycrystalline SnO, which exhibited excellent thermo-oxidative stability might be a good candidate as a p-type oxide material for photoelectric applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...