CRISPR/Cas-directed programmable assembly of multi-enzyme complexes†
Abstract
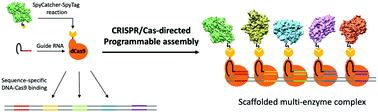
We describe a versatile CRISPR/Cas-based strategy to construct multi-enzyme complexes scaffolded on a DNA template in programmable patterns. Catalytically inactive dCas9 nuclease was used in combination with SpyCatcher–SpyTag chemistry to assemble enzymes in a highly modular fashion. Five enzymes comprising the violacein biosynthesis pathway were precisely organized in nanometer proximity; a notable increase in violacein production demonstrated the benefits of scaffolding.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
