Amyloid-like protein aggregates combining antifouling with antibacterial activity†
Abstract
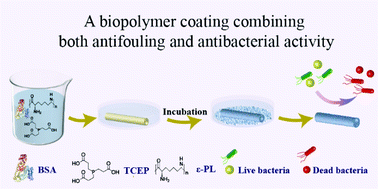
Infections related to implanted medical devices have placed a heavy burden on public health and require feasible solutions. In this study, a simple approach is reported to fabricate an antifouling and antibacterial dual-functional coating. One-step aqueous supramolecular assembly of bovine serum albumin (BSA) is employed to immobilize ε-polylysine (ε-PL) and form a coating (PTB@ε-PL). Based on amyloid-like protein aggregation through the rapid reduction of the intramolecular disulfide bonds of BSA by tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine, a dense PTB@ε-PL nanofilm with controllable thickness and ε-PL loading density can be covered on virtually arbitrary material surfaces by simple aqueous dipping. In vitro and in vivo experiments show that this coating not only exhibits effective antibacterial activity against Gram-positive/Gram-negative bacteria, but also imparts excellent antifouling property to the surface. As a pure biopolymer coating, the PTB@ε-PL nanofilm shows negligible cytotoxicity and hemolysis. In addition, due to the various functional groups exposed on the surface of the nanofilm, the coating shows excellent interfacial bonding stability and can maintain bactericidal and antifouling properties under harsh conditions including ultrasound, autoclaving, organic solvents, and physiological body fluids.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Antibacterial Biomaterials and Biomaterials Science Most Popular 2020


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...