Tumor regression and potentiation of polymeric vascular disrupting therapy through reprogramming of a hypoxia microenvironment with temsirolimus
Abstract
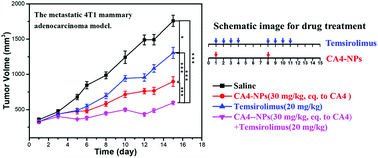
Although the polymeric vascular disrupting agent (poly(L-glutamic acid)-graft-methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)/combretastatin A4) nanoparticles (CA4-NPs) has great potential to inhibit cancer growth, it is still a challenge to avert tumor recurrence and metastasis after treatment. It is mainly tightly associated with hypoxia induced by CA4-NPs, which can activate many downstream genes regulating tumor growth and metastasis. Herein, to relieve a tumor hypoxia microenvironment, the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus was employed to modulate the tumor microenvironment when treated with CA4-NPs. In vitro MTT experiments strongly verified that the combination of temsirolimus with polymeric CA4-NPs exhibited an additive toxicity to 4T1 cells. An in vivo study with the 4T1 mammary adenocarcinoma model revealed that consistent with the proposed scenario, combination therapy with CA4-NPs plus temsirolimus suppressed tumor growth significantly more strongly compared to either CA4-NPs or temsirolimus monotherapy, and the inhibition rate to 4T1 tumor with a volume of 300 mm3 was 71%. The mechanism underling combination treatment was confirmed by western blotting and immunofluorescence staining, and the results demonstrated that temsirolimus could inhibit HIF1α expression. Thus, this work provides a mechanistic rationale for the use of VDAs in combination with the mTOR inhibitor to enhance anticancer efficacy, delaying tumor recurrence and inhibiting tumor metastasis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...