Comparison of activation processes for 3D printed PLA-graphene electrodes: electrochemical properties and application for sensing of dopamine†
Abstract
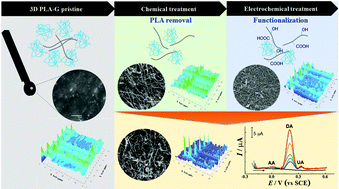
This paper reports the comparison of the electrochemical properties of 3D PLA-graphene electrodes (PLA-G) under different activation conditions and through different processes. In this work, the performance of the electrodes was evaluated after polishing, electrochemical and chemical treatments and a combination of them. The best results were obtained with hydroxide activation using 1.0 mol L−1 NaOH for 30 min of immersion, which promoted the saponification of PLA exposing the graphene nanoribbon structures. The improvement was more evident also after electrochemical activation, which led to a great increase in surface area, defects, electron transfer rate and amount of edge sites. The analytical performance of the proposed PLA-GNaOH-30-EC electrode was evaluated in the presence of dopamine (DA) by three electrochemical techniques, presenting a broad linear range, and limits of detection of 3.49, 2.17 and 1.67 μmol L−1 were obtained by cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and square wave voltammetry (SWV), respectively. The separation and quantification of DA in the presence of AA and UA was also reported. The sensor showed good repeatability and reproducibility and was successfully applied to DA determination in synthetic urine and human serum, showing good recovery, from 88.8 to 98.4%. Therefore, the activation methods were essential for the improvement in the 3D PLA-G electrode properties, allowing graphene surface alteration and electrochemical enhancement in the sensing of molecular targets.
- This article is part of the themed collections: #RSCPoster Conference, Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry and Versatile Electrochemical Approaches


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...