Electro-insertion of Mn2+ ions into V2O5·nH2O on MWCNTs coated carbon felt for binder-free Na+ ion battery electrodes†
Abstract
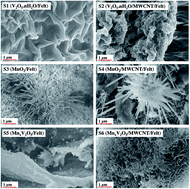
In the present article, we report the electrochemical deposition of hydrated and amorphous V2O5·nH2O nanostructures and related Mn2+ cations insertion during anodic polarization. The hydrated phase was synthesized on hydrophilic carbon felt substrates coated by defective multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). From the combined data of micro-Raman scattering and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), it was possible to see that the Mn2+ cations were intercalated into V2O5 under anodic polarization. When MnOOH is inserted between atomic bilayers of V2O5·nH2O (V5+), a 3D complex monoclinic-MnxV2O5 system arises. This novel method of Mn doping into V2O5·nH2O/MWCNT produces an amorphous MnxV2O5/MWCNT but without hydration. The resulting binder-free MnxV2O5/MWCNT/felt composite electrode provides remarkable Na+ reversible specific capacities of 400 mA h g−1 and 224 mA h g−1 in the 3.5–1.0 V and 3.5–1.5 V ranges, respectively, while the V2O5·nH2O/MWCNT/felt provides only 120 mA h g−1 between the smaller cut-off potential limits. The MnxV2O5/MWCNT nanostructures synthesis onto fibers of graphitic felt does not present a fading capacity during the polarization of 100 discharge/charge cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...