ATP fosters the tuning of nanostructured CeO2 peroxidase-like activity for promising antibacterial performance†
Abstract
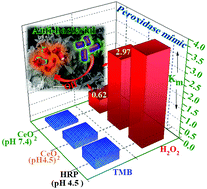
An enduring and formidable challenge in nanozyme catalysis is low sensitivity and operational instability, which impedes their biological usage. In this contribution fluorite-structured cerium oxide nanocrystals (CeO2 NCs) with ∼23.04% Ce3+ fraction were found to possess recyclable (10 cycles) peroxidase (POD)-like activity capable of catalyzing the oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) when hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) serves as oxidant, and exhibit high substrate affinity under acidic conditions. We tuned this catalytic activity at neutral pH (7.4) using adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It was found that ATP stabilizes the oxidation product and improves catalytic performance at neutral pH. Mechanistic investigation reveals that oxidation of TMB originates from catalyst (CeO2 NCs)-directed decomposition of H2O2, which pools hydroxyl (˙OH) radicals under acidic and neutral environments; kinetic studies indicate a Michaelis–Menten enzyme kinetic model. Notably, above pH 4.5, ATP facilitates a drop in catalyst Km values of about 2.5 and 4.79 times for TMB and H2O2, respectively, suggesting high affinity favouring reaction feasibility at neutral pH. Screening of other relevant modulators shows the following order in promoting catalysis at neutral pH: ATP > histidine ≥ ADP >AMP. This pH-tunable POD-mimic CeO2 nanozyme realizes a nanocatalytic strategy for sourcing ˙OH radicals, which contributes to anti-bacterial performance. This study provides new insight for designing nanozymes and expanding the use of nanozymes in biomedicine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...