The effect of side-chain length on the microstructure and processing window of zone-cast naphthalene-based bispentalenes†
Abstract
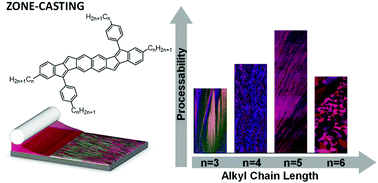
The solubilizing side-groups of solution-processable π-conjugated organic semiconductors affect both the crystal structure and microstructure of the respective thin films and thus charge-carrier mobility in devices. In this work, we explore how the alkyl side-chain length influences thin-film structure and charge transport in field-effect transistors of zone-cast, naphthalene-based bispentalenes. By tuning the alkyl-chain length and the casting speed, we alter the microstructure from highly aligned ribbons, to feathered ribbons, to disordered grains. Concurrently, the hole mobility changes over two orders of magnitude, from 0.001 cm2 V−1 s−1 at the fastest speeds to roughly 0.1 cm2 V−1 s−1 at slower speeds. The highest mobilities correspond to the presence of an aligned ribbon morphology. While optical measurements indicate negligible electronic differences between the molecules, grazing incidence X-ray diffraction measurements show that the films display different degrees of order and alignment. The compound with pentyl side-chains exhibits the largest tolerance to different processing conditions, yielding an aligned ribbon microstructure and high mobility over a wide range of casting speeds. Our results highlight the impact that even small changes to the molecular structure can have on the processing window and transport properties of thin-film devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 EES Lectureship Winner: Yana Vaynzof


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...