Single-phase white-emitting phosphors based on apatite-type gadolinium silicate, Gd9.33(SiO4)6O2 doped with Dy3+, Eu3+ and Tb3+†
Abstract
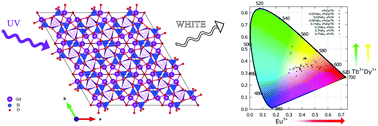
Two series of new apatite-type silicate materials were synthesised and characterised with the aim of achieving white light emission from single-phase phosphors. The Gd9.33(SiO4)6O2 host was doped systematically with Dy3+, Tb3+ and Eu3+ to tune the emission to the white light region. Eight new phosphors with emission very near the ideal white light point are reported. The best properties are found for the 0.5%Tb, 0.03%Eu co-doped Gd9.33(SiO4)6O2, with colour coordinates (0.340, 0.341) and a correlated colour temperature of 5190 K, corresponding to the white light region. The temporal decay of emission from the doped ions was measured following pulsed excitation of the Gd3+ host. An evaluation of energy transfer and quenching effects in the phosphors has been made based on the lifetimes so obtained. In particular, a comparison of the Eu3+ lifetimes in the Dy,Eu co-doped phosphors with those in the Tb,Eu-containing materials suggests quenching of the 5D0 excited state of Eu3+ by the Dy3+ ions. These observations imply that the combination of Eu3+ and Dy3+ ions may not provide optimal efficiencies in phosphors, and that the combination of Eu3+ and Tb3+ is likely to be superior for optimising the emission properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...