Fabrication of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by solvent alteration and their bactericidal applications†
Abstract
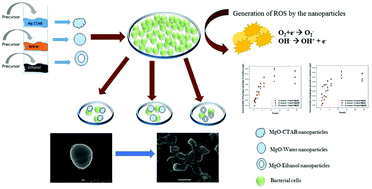
The ever-increasing resistance of pathogens towards antibiotics has resulted in the development of novel antibacterial materials. In this work, magnesium oxide nanoparticles were synthesized and the synthesis parameters played an important role in determining the physico-chemical properties of the nanoparticles. Three reaction solvents (water, ethyl alcohol and aqueous cetrimonium-tetrabromide) were employed and the morphological, surface and antibacterial properties of the resultant nanoparticles were compared. The use of ethanol yielded a smaller particle size (∼10 nm) and thus a greater surface area than that of CTAB (∼17 nm) or water (∼28 nm). The antibacterial efficacy of these nanoparticles was proven by the increase in cell reduction against both S. aureus and E. coli. About 3-log reduction in the bacterial count was observed using a concentration of 5 mg ml−1 of MgO synthesized in ethanol. The logistic growth model equation was used to fit the growth kinetics of the treated bacteria and the parameters also changed significantly with the solvent. The generation of reactive oxygen species was found to be time- and concentration-dependent and the haemolysis of the nanoparticles was much lower than the allowable limit. Confocal and scanning electron microscopies were employed for morphological insights into the treated bacteria, thus proving the use of these nanoparticles in biomedicine.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Most Popular Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...