Inverted planar perovskite solar cells based on CsI-doped PEDOT:PSS with efficiency beyond 20% and small energy loss †
Abstract
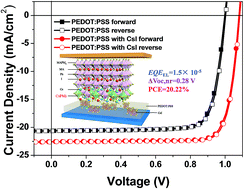
PEDOT:PSS is widely used in perovskite solar cells (PSCs) as the most popular hole transporting layer (HTL). However, p-i-n type inverted planar PSCs based on the PEDOT:PSS HTL typically exhibit up to 200 mV more voltage loss compared to conventional planar PSCs (n-i-p) that generally show open circuit voltages (VOC) of around 1.1 V. In this study, we develop a simple, inexpensive and effective interfacial engineering strategy by doping PEDOT:PSS with cesium iodide (CsI) to reduce the voltage loss and achieve highly efficient inverted PSCs. SEM, AFM, and XPS measurements suggest that CsI modifies the interface between PEDOT:PSS and perovskite by reacting with PbI2 to form CsPbI3, thus facilitating interfacial contact and charge transport. Moreover, after CsI-modification (CsI-PEDOT:PSS), the hole transport properties of PEDOT:PSS and the hole extraction are enhanced, while the energy levels are more favorable and charge recombination is suppressed. Importantly, compared to pristine PEDOT:PSS that suffers from a large non-radiative recombination loss (0.375 V), CsI-PEDOT:PSS makes the device to realize an impressively low non-radiative voltage loss (only 0.287 V). As a result, inverted PSCs based on CsI-PEDOT:PSS show a small voltage loss, an excellent power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 20.22%, and no hysteresis and achieve a high VOC (1.084 V), while the control device without CsI shows an inferior efficiency of 16.57%. Both the high VOC and PCE are an improvement over literature data on modified PEDOT:PSS-based inverted PSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...