Ultrahigh energy-storage density in A-/B-site co-doped AgNbO3 lead-free antiferroelectric ceramics: insight into the origin of antiferroelectricity†
Abstract
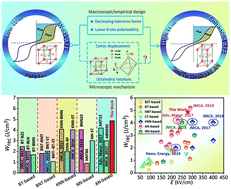
Lead-free dielectric capacitors have tremendous potential for energy storage applications due to their stable and fast charge–discharge performances in comparison to supercapacitors and batteries. One of the key limitations to today's lead-free dielectric capacitors, however, is the low energy storage density. In this work, we show that the stability of antiferroelectric characteristics can be significantly improved by chemical co-substitution with Sm3+ and Ta5+ ions in the A- and B-site, respectively. As a consequence, a remarkably improved energy storage density up to 4.87 J cm−3 was achieved in (Sm0.02Ag0.94)(Nb0.9Ta0.1)O3 ceramics, which also exhibited good thermal stability with variations <5% in the temperature range of 20 to 140 °C. Structural resolution revealed that reducing both the ionic radius of A-site ions and the electronic polarizability of B-site ions contributes to lattice volume contraction. Consequently, the cation displacement and [Nb/TaO6] octahedral tilting angle were restricted, leading to a significant enhancement in antiferroelectricity and energy storage density. Our study provides an intriguing opportunity for the design of antiferroelectric materials with potentially good energy storage performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...