Role of pendant side-chain length in determining polymer 3D printability†
Abstract
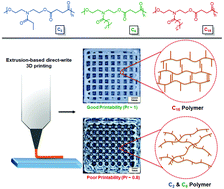
Three-dimensional (3D) printing allows for creation of patient-specific implants. However, development of new synthetic materials for 3D printing has been relatively slow with only a few polymers available for tissue engineering applications. Most of these polymers require harsh processing conditions like high temperatures and pressures or are mixed with a combination of leachable additives like plasticizers, initiators, crosslinkers, and solvents to enable 3D printing. Therefore, to propel the development of new polymers for ambient temperature, additive-free 3D printing it is necessary to systematically understand the relationship between the structure of a polymer with its 3D printability. Herein, three homopolyesters were synthesized, each with a common backbone but differing in the length of their saturated, aliphatic pendant chains with 2, 6, or 15 carbons. The physical properties such as the glass transition temperature (Tg) and the rheological properties like shear thinning, temperature response, and stress relaxation were correlated to the individual polymer's 3D printability. The 3D printability of the polymers was assessed based on four criteria: ability to be extruded as continuous filaments, shape fidelity, the retention of printed shape, and the ability to form free hanging filaments. We observed that the polymers with longer side chains can be extruded at low temperature and pressure because the long side chains act as internal diluents and increase the flowability of the polymer. However, their ability to retain the 3D printed shape is adversely affected by the increase in side chain length, unless the side chains form ordered structures leading to immediate recovery of viscosity. The insight derived from the systematic investigation of the effect of polymer structure on their rheology and 3D printability can be used to rationally design other polymers for extrusion-based direct-write 3D printing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...