Proteinase-sculptured 3D-printed graphene/polylactic acid electrodes as potential biosensing platforms: towards enzymatic modeling of 3D-printed structures†
Abstract
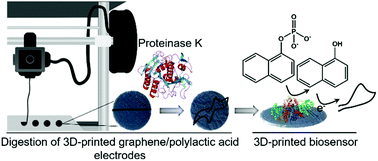
3D printing technologies are currently appealing for the research community due to their demonstrated versatility for different scientific applications. One of the most commonly used materials for 3D printing is polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable polymer that can be fully or partially digested by enzymes such as proteinase K. This work seeks to exploit PLA's biodegradability to selectively and reproducibly sculpt 3D-printed graphene/PLA surfaces to turn them into sensitive electroactive platforms. Proteinase K-catalyzed digestion of 3D-printed graphene/PLA electrodes is proposed as an environmentally friendly, highly controllable, and reproducible activation procedure of 3D-printed electrodes. Proteinase K digests PLA in a controllable fashion, exposing electroactive graphene sheets embedded within the 3D-printed structures to the solution and therefore achieving a tailorable electrode performance. A proof-of-concept biosensing application is proposed, based on the immobilization of enzyme alkaline phosphatase at the sculptured electrodes with the subsequent electrochemical detection of 1-naphthol in aqueous media. This work attempts to continue demonstrating the potential of 3D printing in electroanalytical applications, as well as to explore the exciting possibilities arising from merging biotechnological processes with these manufacturing procedures.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanocarbons


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...