Induction of chirality in 4,4′-azopyridine by halogen-bonding interaction with optically active ditopic donors†
Abstract
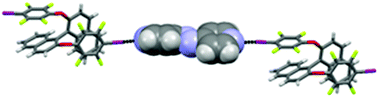
Optically active ditopic halogen bond donors bearing two 4-iodotetrafluorophenyl groups were obtained by reaction of chiral diols with iodopentafluorobenzene. Co-crystallization of these donors with anti-4,4′-azopyridine afforded binary complexes containing infinite chains of the alternating component molecules connected by halogen bonds. The solid state CD measurements confirmed that complexation induces optical activity of the azo chromophore due to the twisting of the aryl-N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N system or external chiral perturbation exerted by host molecules.
N system or external chiral perturbation exerted by host molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...