Fabrication of 2D heterojunction photocatalyst Co-g-C3N4/MoS2 with enhanced solar-light-driven photocatalytic activity
Abstract
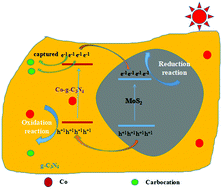
A novel 2D heterojunction composite photocatalyst Co-g-C3N4/MoS2 obtained by coupling Co-doped g-C3N4 and MoS2 nanosheets has been successfully fabricated via a facile impregnation and calcination method. The results of photocatalytic experiments showed that the as-prepared catalyst exhibited markedly enhanced photocatalytic activity. The rates for the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) and hydrogen evolution under simulated sunlight irradiation using a catalyst were about 6.4 and 4.7 times higher than those of pristine g-C3N4. Moreover, the photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared product was compared with that of the 2D heterojunction g-C3N4/MoS2 or Co-doped g-C3N4 only. It was revealed that the photocatalytic activity of Co-g-C3N4/MoS2 was better than those of g-C3N4/MoS2 and Co-g-C3N4. The great improvement in photocatalytic activity performance is mainly ascribed to the Co-doping and formation of a 2D heterojunction, resulting in a fast charge carrier transfer, effective suppression of recombination of charge carriers, and an increase of light absorption. The doping amount of cobalt and the loading amount of MoS2 have a great influence on the photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4, and they were studied in detail. The present work reveals that the combination of the formed-2D heterojunction with Co-doping should be a good strategy to boost the solar-light-driven photocatalytic activity of semiconductor catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...