Quantitative speciation analysis for the in vivo study of iron metabolism and bioavailability from formula milk fortified with stable isotope enriched iron oxo-hydroxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
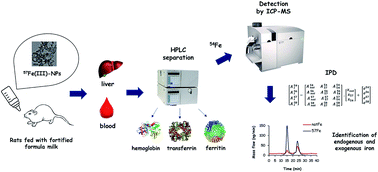
For the first time, the study of iron metabolism and bioavailability, administered as stable iron isotope enriched nanoparticles, was carried out by speciation analysis and isotope pattern deconvolution (IPD) in rat body fluids and tissue. Nanoparticles of Fe(III) oxo-hydroxide were synthesized using a stable iron isotope (57Fe) and administered to lactating rats as a fortifier in formula milk. Quantitative iron speciation analysis in erythrocytes, serum and rat liver was performed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to post-column isotope dilution and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The quantification of endogenous (natural Fe) and exogenous iron (57Fe) was carried out by applying the IPD methodology. The speciation analysis demonstrated that 57Fe was incorporated into the iron compartments (functional, transport and storage) and was associated with the main proteins implicated in iron metabolism (hemoglobin, transferrin and ferritin-like species). Results showed that the iron administered as labeled nanoparticles was incorporated in a high degree (more than 50%), being higher than the degree observed for ferrous sulfate, the most common iron fortifier.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Community Leaders: Alfredo Sanz-Medel


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...