Selenoneine and ergothioneine in human blood cells determined simultaneously by HPLC/ICP-QQQ-MS†
Abstract
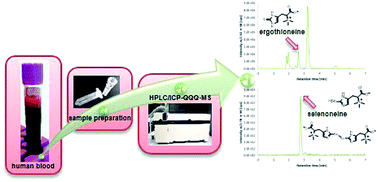
The possible relevance to human health of selenoneine and its sulfur-analogue ergothioneine has generated interest in their quantitative determination in biological samples. To gain more insight into the similarities and differences of these two species, a method for their simultaneous quantitative determination in human blood cells using reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) coupled to inductively coupled plasma triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-QQQ-MS) is presented. Spectral interferences hampering the determination of sulfur and selenium by ICPMS are overcome by introducing oxygen to the reaction cell. To access selenoneine and ergothioneine in the complex blood matrix, lysis of the cells with cold water followed by cut-off filtration (3000 Da) is performed. Recoveries based on blood cells spiked with selenoneine and ergothioneine were between 80% and 85%. The standard deviation of the method was around 0.10 mg S per L for ergothioneine (corresponding to relative standard deviations (RSD) between 10–1% for ergothioneine concentrations of 1–10 mg S per L) and 0.25 μg Se per L for selenoneine (RSDs of 25–2% for concentrations of 1–10 μg Se per L). The method was applied to blood cell samples from three volunteers which showed selenoneine and ergothioneine concentrations in the range of 3.25 to 7.35 μg Se per L and 0.86 to 6.44 mg S per L, respectively. The method is expected to be of wide use in future studies investigating the dietary uptake of selenoneine and ergothioneine and their relevance in human health.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...