Synthesis of levulinic acid based poly(amine-co-ester)s†
Abstract
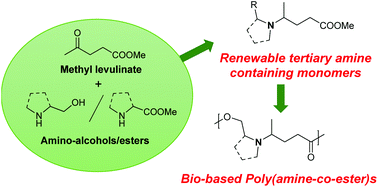
Four novel biobased monomers (i.e. two diesters and two hydroxyesters) bearing a tertiary amine in their backbone have been synthesized from the sustainable methyl levulinate and amino-alcohols/amino-esters derived from natural amino acids. Their homopolymerization/copolymerization with diols leads to six poly(amine-co-ester)s with various microstructures. These families of biodegradable polyesters have been reported to be efficient carriers for gene delivery. The polymers are carefully characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H and 13C NMR) and size exclusion chromatography (SEC), and exhibit molecular weights (Mn) up to 36 kg mol−1 and dispersities (Đ) between 1.5 and 2.1. They also present good solubility in aqueous acidic media due to amine protonation. Such properties are promising for applications in the biomedical field or in personal care products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...