Anti-melanogenesis properties of condensed tannins from Vigna angularis seeds with potent antioxidant and DNA damage protection activities
Abstract
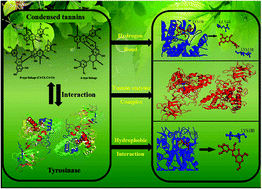
Condensed tannins contained in food are known to have many beneficial impacts on human health. In this study, we attempt to evaluate the structural features, antityrosinase effects, anti-melanogenesis properties, antioxidant activity and DNA damage protection activity of condensed tannins purified from the seeds of Vigna angularis (Willd.) Ohwi et Ohashi. MALDI-TOF MS, ESI-Full-MS, and HPLC-ESI-MS demonstrated that condensed tannins are composed of procyanidins, prodelphinidins and their gallates, among which procyanidins are the dominant components. As reversible and mixed-type inhibitors of tyrosinase, condensed tannins from V. angularis strongly inhibited the monophenolase and odiphenolase activities with IC50 values of 130.0 ± 0.5 and 35.1 ± 2.0 μg mL−1, respectively. What's more, condensed tannins had a good inhibitory effect on cell proliferation, cellular tyrosinase activity, and melanogenesis of B16 mouse melanoma cells. Based on fluorescence quenching analyses, these compounds were determined to be effective quenchers of the enzyme and its substrates. According to molecular docking, the strong interaction between condensed tannins and tyrosinase was mainly driven by hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic force. In addition, condensed tannins showed a powerful antioxidant capacity and DNA damage protection activity. Therefore, condensed tannins from V. angularis have feasible applications in food, medicine, and the cosmetics industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...