Dietary wild bitter gourd displays selective androgen receptor modulator like activity and improves the muscle decline of orchidectomized mice†
Abstract
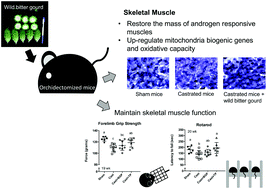
Loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength is often associated with disability and poor quality of life. Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) are under development as potential treatment. This study aims at examining the potential of wild bitter gourd (BG) as a SARM and its effects on the muscle decline induced by orchiectomy. In the cell-based androgen receptor (AR) transactivation assay, the BGP extract showed weak agonistic and antagonistic activities, resembling those of some SARMs. Male C57BL/6J mice were sham-operated (Sham group) or castrated (Cast groups) and fed a modified AIN-93G high sucrose diet supplemented without (Cast group) or with 5% lyophilized BG powder (Cast + BGP) or with testosterone propionate (7 mg TP per kg diet, Cast + TP) for 23 weeks. In contrast to the Cast + TP group, the BGP supplementation did not affect the serum testosterone concentration, and prostate and seminal vesicle mass. Both TP and BGP supplementation increased the weight of androgen responsive muscles, bulbocavernosus (BC) and levator ani (LA) (p < 0.05). The grip strength and the performance on a rotarod of the Cast + BGP group were comparable to those of the Cast + TP group (p > 0.05). The number of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-positive fibers of the Cast + BGP group was not significantly different from that of the Sham and Cast + TP groups (p > 0.05). The BGP supplementation up-regulated the Pgc1α, Ucp2 or Ucp3 gene expressions in skeletal muscles of castrated mice (p < 0.05). BGP showed some characteristics of the SARM and might improve skeletal muscle function through the up-regulation of mitochondrial biogenic genes and oxidative capacity, and ameliorated the castration-induced decline of skeletal muscle function in mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...