Towards durable practical lithium–metal batteries: advancing the feasibility of poly-DOL-based quasi-solid-state electrolytes via a novel nitrate-based additive†
Abstract
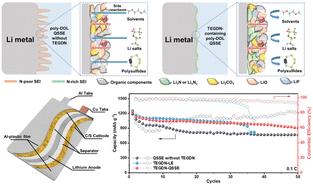
The in situ polymerization of quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs) is emerging as a promising approach for the development of scalable, safe, and high-performance quasi-solid-state lithium–metal batteries. In this context, poly-DOL-based electrolytes are particularly attractive due to their wide electrochemical window and strong compatibility with lithium metal. To enhance the stability of lithium metal, LiNO3 is frequently added as it creates an effective, Li3N-rich solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode. However, LiNO3 prevents DOL's ring-opening polymerization, making the two compounds incompatible. To address this issue, this work develops triethylene glycol dinitrate (TEGDN), a novel nitrate-based additive, to replace LiNO3. Like LiNO3, TEGDN forms a dense, nitrogen-rich solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of lithium, protecting it from parasitic reactions. However, unlike LiNO3, TEGDN does not interfere with the polymerization of DOL, allowing the fabrication of a highly effective electrolyte that delivers an ionic conductivity of 2.87 mS cm−1 and an oxidation stability potential of 4.28 V at room temperature. To demonstrate the viability of this approach, a Li|LiFePO4 coin-type cell cycling stably more than 2000 times at 1C is fabricated. In addition, a 1.7 A h pouch-type lithium-sulfur cell with an initial specific energy of 304 W h kg−1 and a capacity retention of 79.9% after 50 cycles is prepared. In short, the present study proposed a new additive to resolve poly-DOL and LiNO3 incompatibility for the first time and developed in situ polymerized quasi-solid-state batteries that exhibit remarkable capacity and stability by forming an N-rich solid electrolyte interphase.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...