Chronic exposure to graphene oxide (GO) induced inflammation and differentially disturbed the intestinal microbiota in zebrafish†
Abstract
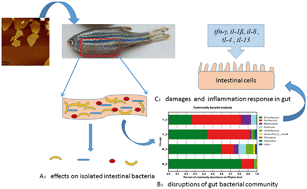
Graphene oxide (GO) has been extensively used in various critical fields such as biomedicine, while its antibacterial properties and potential toxicities raised serious concerns in recent years. The impacts of GO on the intestinal microbiota and associated immune responses in the host are still ambiguous. In this study, we investigated the effects of GO chronic exposure (25 days) on the composition of the intestinal microbiota and immune response in female & male zebrafish at different concentrations (0.05, 0.5, and 5 mg L−1). Results demonstrated that the diversity and richness of the bacterial community at the phylum and genus levels significantly differed in the presence of GO between female and male zebrafish. The in vitro assay verified the effect of acute toxicity of GO on the survival ability of bacterial strains isolated from zebrafish intestines, albeit no changes in the bacterial metabolic functions were observed. Further, exposure to GO significantly altered the length and width of villi in the anterior intestines, caused abnormalities of the ultra-micro structure, and increased the number of inflammation-related cells detected by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Moreover, the elevated expression levels of crucial pro-inflammatory genes, such as tnf-α, ifn-γ, nf-κb, tlr-5, il-1β, and il-8, were significantly induced, while the expression levels of anti-inflammatory genes, such as il-4 and il-13, were inhibited, especially in male zebrafish. Taken all together, chronic exposure to GO disturbed the diversity and richness of intestinal microbes, increased the pathogenic bacterial community in zebrafish, induced damage to the gut tissues, and activated the inflammation response. These findings provided new insights into GO effects on the inflammation and intestinal microbiota in the host, which is closely linked with metabolisms and physiological activities in biological systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...