Fenton-based treatment of electroless copper plating waste for organics mineralization and CuO recovery†
Abstract
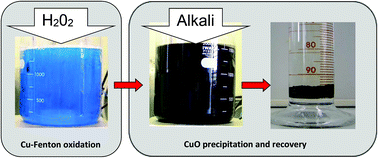
Fenton-based oxidation was used to treat an actual electroless copper plating waste solution containing a mixture of organic compounds including tartaric acid, formaldehyde and formic acid. As a novel advancement, the naturally present Cu(II) ions were directly used as a catalyst. An external metal ion, particularly Fe(II), was not required and only hydrogen peroxide was added to generate oxidizing hydroxyl radicals. During treatment, a substantial increase in solution temperature was observed as a result of tartaric acid degradation and the highly exothermic process enhanced the decomposition of formaldehyde and formic acid. The major organic components were completely mineralized, leaving only a small amount of oxalic acid. By the Cu-Fenton, close to 99% TOC and COD removal was achieved. The high temperature oxidation also led to the almost complete removal (<0.1 ppm residual) and recovery of Cu ions as a low volume CuO precipitate during alkalinization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...