Construction of an artificial inorganic leaf CdS–BiVO4 Z-scheme and its enhancement activities for pollutant degradation and hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
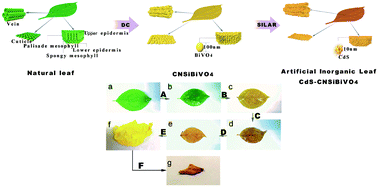
The natural photosynthesis of plants is closely related to leaf structures, therefore, the preparation of photocatalysts with leaf-like structures is of great significance to improve the activity of artificial photosynthetic systems. Using the leaves of a Chongyang wood seedling as the biological template (BT), artificial inorganic leaf CdS–BiVO4 was constructed by the “biological template”–“dipping-calcination”–“successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction” (BT–DC–SILAR) method. The fine hierarchical leaf-like structures of the artificial inorganic leaf were confirmed by FE-SEM and TEM observations. In the process of synthesizing the artificial inorganic leaf, the doping of C, N, and Si elements (coming from a natural leaf) was determined by XPS and FTIR analyses. The enhanced optical properties of the artificial inorganic leaf were proved by UV-vis DRS and PL analyses. It was found that the artificial inorganic leaf demonstrated superior photocatalytic activity in both photocatalytic pollutant degradation and H2 evolution. After 2 h of visible light irradiation, the photocatalytic decomposition efficiency of RhB for the artificial inorganic leaf (92%) is 2.1 times higher than that of no template BiVO4 (45%), and the photocatalytic H2 evolution for the artificial inorganic leaf (9250 μmol g−1CdS h−1) is 13 times higher than that of pure CdS (706 μmol g−1CdS h−1). Driven by solar light, the artificial inorganic leaf also possesses a strong artificial photosynthetic activity. The enhanced photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the combined action of the unique structure, the C, N, and Si elemental doping and the formation of the Z-scheme. Based on this research, a new method, BT–DC–SILAR, for the construction of a micro-nano-Z-scheme photocatalytic system was proposed, which enables the simultaneous control of structure, elemental doping and Z-scheme photocatalytic systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...