Catalytic dissociation of tris(dimethylamino)silane on hot tungsten and tantalum filament surfaces†
Abstract
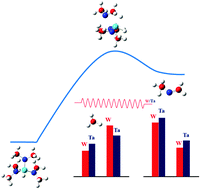
The dissociation of tris(dimethylamino)silane (TrDMAS) on hot tungsten and tantalum surfaces was studied under collision-free conditions. The products from the hot-wire decomposition of TrDMAS were monitored using a 10.5 eV vacuum ultraviolet laser single-photon ionization in tandem with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Formation of a methyl radical and N-methyl methyleneimine (NMMI) was detected. A transition from a surface reaction rate-limiting regime at filament temperatures lower than 1800–2000 °C to mass transport regime at higher temperatures (>1800–2000 °C) was observed for the formation of both products. In the surface reaction regime, the Arrhenius behavior was followed in two separate temperature regions with different activation energies. It was found that low temperatures (900–1300 °C) favor the production of the methyl radical and high temperatures (1400–2000 °C) favor the production of NMMI with lower activation energies. A theoretical investigation using ab initio calculations of the concerted and stepwise formation of NMMI along with the homolytic cleavages of N–CH3 and Si–H in the gas phase has shown that the concerted pathway to form NMMI is the most energetically favorable one of all four routes with an activation barrier of 328 kJ mol−1. The lower activation energy values determined experimentally for the formation of NMMI and ˙CH3 as compared to those obtained from theoretical calculations indicate that the dissociation of TrDMAS, an N-containing organosilicon molecule, on the W and Ta surfaces is a catalytic cracking process.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Photodissociation and reaction dynamics


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...