Co-delivery of d-(KLAKLAK)2 peptide and doxorubicin using a pH-sensitive nanocarrier for synergistic anticancer treatment†
Abstract
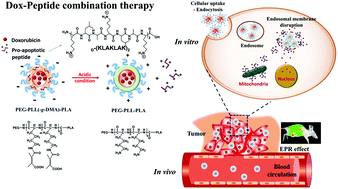
Currently, one of the most important challenges in the development of nanotechnology-based anticancer treatments is the failure of nanoparticles to escape from the endo-lysosomal compartment and the resulting elimination of endocytosed nanoparticles via the exocytosis pathway without drug release. A pH-sensitive nanoparticle composed of poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(L-lysine)(-grafted 2,3 dimethyl maleic anhydride)–poly(lactic acid) triblock copolymer (PEG–PLL(-g-DMA)–PLA) with a pro-apoptotic peptide (D-(KLAKLAK)2) and an anticancer drug doxorubicin (Dox) (DTM(Pep, Dox)) was prepared and evaluated for its antiproliferative activity against tumor cells. Due to the membrane-lytic ability of the peptide and the “proton sponge” effect of the pH-sensitive nanocarrier, DTM(Pep, Dox) accelerated the disruption of the endo-lysosomal membrane and displayed enhanced anticancer activities, arising from strong synergism, under in vitro and in vivo conditions. The prepared formulations are anticipated to be of potential use in nanotechnology-based combination therapy and it is believed that this novel formulation will have new applications in advanced tumor therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...