Efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to CO with high selectivity using a N-doped carbonized wood membrane†
Abstract
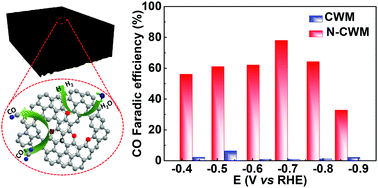
A N-doped carbonized wood membrane (N-CWM) is fabricated and directly used as a self-supported electrode for efficient CO2 electroreduction in aqueous solution with a maximum CO faradaic efficiency (FE) of 78% at −0.68 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) and long-term stability for CO production with an average FE of 67% during 10 h of electrolysis. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal that the pyridinic-N is the most active site for selective CO2 reduction to CO, which can significantly lower the free energy barriers for the formation of COOH* intermediate and CO desorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...