Polyoxometalate-based composite cluster with core–shell structure: Co4(PW9)2@graphdiyne as stable electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution and its mechanism research†
Abstract
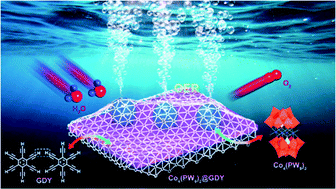
A composite cluster with core–shell structure composed of polyoxometalates (POMs) and graphdiyne (GDY) was synthesized and applied for the electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Compared with the original POMs and GDY, the composite cluster Co4(PW9)2@GDY demonstrates superior performance and stable electrochemical OER. The core–shell composite cluster exhibited high performance for OER with low potentials and a small Tafel slope. Moreover, high catalytic activity of the cluster was achieved at a high current density. Co4(PW9)2@GDY has excellent catalytic performance and long stability due to its strong electron-transfer ability in the system, higher conductivity, and the structural advantage of pores in GDY. We also tested the OER synergism mechanism between POM and GDY. This would open access and guide us to synthesize novel clusters based on polyoxometalates and graphdiyne.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...