Bifidobacterium longum relieves constipation by regulating the intestinal barrier of mice†
Abstract
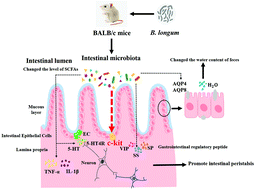
Constipation is a major health concern worldwide, requiring effective and safe treatment options. This study mainly focused on three species and nine strains of bifidobacteria from different sources to study their abilities to relieve constipation induced by loperamide in BALB/C mice. By monitoring constipation-related indicators, it was found that only Bifidobacterium longum (B. longum) relieved constipation, which indicated that bifidobacteria had inter-species differences in relieving constipation. Furthermore, through the detection of biological, chemical, mechanical, and immune barriers in mice, it was discovered that B. longum upregulates the relative abundance of 22 genera that were positively related to faecal water content, small intestinal propulsion rate, acetate, propionate, and intestinal mechanical barrier and negatively correlated with inflammatory factors, AQP8 and the time of first black stool and downregulates the relative abundance of Akkermansia. Furthermore, it increased the level of acetate in faeces and reduced the expression of AQP8 in the colon. This enhances intestinal motility and improves water and electrolyte metabolism. Meanwhile, it inhibited inflammation and prevented loperamide-induced intestinal barrier damage in constipated mice by upregulating occludin and downregulating IL-1β and TNF-α. In summary, B. longum relieved constipation by regulating the intestinal barrier in constipated mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...