Determination of rutin by chemiluminescence based on a luminol–potassium periodate–ZnSe system
Abstract
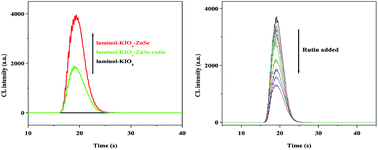
ZnSe quantum dots (QDs) with a homogeneous size distribution and good stability were synthesized by the reaction of zinc acetate and NaHSe in the presence of glutathione (GSH). The obtained ZnSe QDs were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). Simultaneously, UV-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) was performed and the fluorescence properties of ZnSe QDs were investigated. The effect of ZnSe QDs on the luminol–potassium periodate (KIO4) chemiluminescence (CL) system, a popular model CL system, was researched. It was found that as-prepared ZnSe QDs could strongly enhance the chemiluminescence (CL) of the luminol–KIO4 system. To discuss the mechanism of the CL enhancement, we studied the UV-vis and CL spectra of the luminol–KIO4–ZnSe QDs system. The CL enhancement should be attributed to the oxidation of luminol to its excited state by KIO4, under the catalysis of ZnSe QDs, which caused strong light emission. It was found that rutin, p-t-butylprocatechol, catechol, paracetamol, resorcinol and tryptophan could markedly inhibit the CL of the luminol–KIO4–ZnSe QDs system among 17 kinds of amino acids and 23 other kinds of organics. The above phenomena presented good linear relations. Thus, effective methods to detect them were developed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...