Nano-sized paramagnetic and fluorescent fluorinated carbon fiber with high NIR absorbance for cancer chemo-photothermal therapy†
Abstract
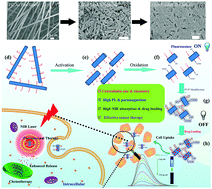
Nano-sized fluorinated carbon fiber possesses unique charge distribution and special chemical bonds and holds great promise in biomedicine. However, its synthesis remains a big challenge on account of the chemical inertness and strong hydrophobicity of C–F bonds. Herein, an up-bottom method to prepare nano-sized and water-soluble fluorinated carbon fiber oxide (FCO) with tunable lengths and adjustable fluorine levels was first developed. It was found that the effective control over structure and composition endowed the FCO with high photoluminescence (PL) and near-infrared (NIR) light absorbance, which was further employed to monitor the drug loading by turn-off PL and treat cancer by photothermal therapy (PTT). We also reported the first experimental example of paramagnetic FCO, whose novel paramagnetism was generated by point defects from fluorine invasion. Moreover, the FCO was noncovalently functionalized with polyvinylpyrrolidone, loaded with doxorubicin of high capacity (1.15 mg mg−1) and exhibited acid-triggered and photothermally enhanced drug release behavior. The application of FCO in cancer treatment achieved much better therapeutic effects than single chemotherapy or PTT. This work established FCO as a novel nano-carrier with high PL, NIR absorbance, paramagnetism, and drug loading capacity, and demonstrated its first application in cancer chemo-photothermal therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Year of the Periodic Table : Low Dimensional Carbon Systems


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...