Structure and rheology of polyelectrolyte complex coacervates†
Abstract
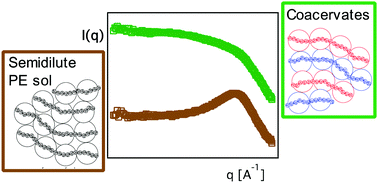
Scattering investigations of the structure and chain conformations, and the rheological properties of polyelectrolyte complexes (PECs) comprising model polyelectrolytes are presented. The use of charged polypeptides – (poly)-lysine and (poly)-glutamic acid with identical backbones allowed for facile tuning of the system parameters, including chain length, side-chain functionality, and chirality. Systematic studies using small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) of liquid PEC coacervates revealed a physical description of these materials as strongly screened semidilute polyelectrolyte solutions comprising oppositely charged chains. At the same time, solid PECs were found to be composed of hydrogen-bonding driven stiff ladder-like structures. While the coacervates behaved akin to semidilute polyelectrolyte solutions upon addition of salt, the solids were largely unaffected by it. Rheology measurements of PEC coacervates revealed a terminal relaxation regime, with an unusual plateauing of the storage modulus at low oscillation frequencies. The plateau may be ascribed to a combination of instrumental limitations and the long-range electrostatic interactions contributing to weak energy storage modes. Excellent superposition of the dynamic moduli was achieved by a time-salt superposition. The shift factors, however, varied more strongly than previously reported with added salt concentration.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Complex Coacervation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...