Mechanical activation in reduced graphite oxide/boron nitride nanocomposite electrocatalysts for significant improvement in dioxygen reduction†
Abstract
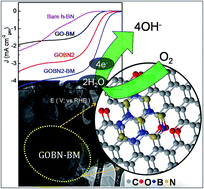
A nanocomposite of reduced graphite oxide (rGO) with hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is prepared using a simple hydrothermal method. Significant enhancement in the surface area of the composite is mainly due to the pre-mechanical activation of pristine GO. The structural and morphological study reveals the formation of a homogeneous nanocomposite and masking of rGO sheets over micron sized h-BN particles respectively. Interestingly, the as-synthesized GOBN2–BM composite (nanocomposite of 2 wt% h-BN with mechanically activated GO) catalyst exhibits significant oxygen electroreduction kinetics in terms of onset potential (Eonset = 0.89 V), half-wave potential (E1/2 = 0.74 V) and limiting current density (JL = 4.4 mA cm−2) with a single step ∼4-electron transfer pathway in alkaline medium. Though the composite catalysts exhibit higher overpotential (110 mV) than state-of-the-art Pt/C catalysts, they are much superior to previously reported carbon or h-BN based nanocomposite electrocatalysts. Importantly, the GOBN2–BM nanocomposite shows excellent tolerance towards both methanol oxidation and CO poisoning. Moreover, the nanocomposite catalysts show substantially higher stability than Pt/C catalysts even after 5000 cycles under similar conditions. Additionally, they show a better relative current stability (95% retention) than that of a Pt/C catalyst, signifying immense selectivity and durability towards oxygen electroreduction kinetics. The electrocatalytic oxygen reduction activity of the nanocomposite is mainly attributed to the high surface area (thanks to mechanical activation of GO, leading to increased pore distribution) as well as the synergistic mechanism between the h-BN and carbon network of rGO. Hence, it could be a potential cathode catalyst to replace precious-metal based catalysts in alkaline fuel cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...