Development of a 3D graphene aerogel and 3D porous graphene/MnO2@polyaniline hybrid film for all-solid-state flexible asymmetric supercapacitors†
Abstract
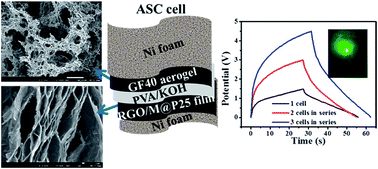
There is an increasing demand for safe, environmentally benign energy storage devices in portable electronic appliances, wearable gadgets, flexible displays, and other personal multimedia devices. In this study, we have fabricated an all-solid-state flexible asymmetric supercapacitor using a novel 3D porous reduced graphene oxide/manganese dioxide@polyaniline (RGO/MnO2@PANI) hybrid film as the positive electrode and a self-assembled 3D pillared graphene aerogel as the negative electrode material with a polyvinyl alcohol/potassium hydroxide (PVA/KOH) gel electrolyte. The flexible composite film was synthesized by vacuum filtration of GO and a MnO2@PANI mixture followed by chemical reduction of the resulting film in a hydrothermal autoclave. The 3D graphene aerogel was synthesized by a hydrothermal route using a solution of the nonionic triblock copolymer Pluronic F-68 as a soft template and vitamin C as a reducing agent. Herein, the Pluronic copolymer played dual roles: first, it enabled the effective dispersion of graphene oxide in water, and second, it assisted the formation of a stable 3D pillared hydrogel assembly. The RGO/MnO2@PANI-based symmetric supercapacitor shows a high energy density of 18.33 W h kg−1 at a power density of 0.388 kW kg−1. An asymmetric supercapacitor (graphene aerogel//RGO/MnO2@PANI), which was fabricated by optimizing the individual electrode materials, exhibited a very high energy density of 38.12 W h kg−1 at a power density of 1.191 kW kg−1 utilizing a large potential window of 1.5 V. Moreover, 3 cells connected in series successfully lit up a red LED for 45 s and displayed similar performance under bending conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...