Paramagnetism enhancement by in situ electrochemical hole doping into a Prussian Blue thin film†
Abstract
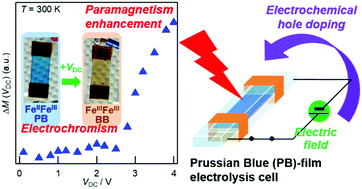
A Prussian Blue (PB) film formed on an indium tin oxide substrate was incorporated in an electrolysis cell with an ionic-liquid midlayer (N,N-diethyl-N-methyl-N-(2-methoxyethyl)ammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide) as an electrolyte. The ionic-liquid electrolysis cell mounted on a SQUID magnetometer was examined under DC bias voltage up to 4.0 V by injecting the charge carriers electrochemically into the PB film. Electrochemical hole doping increased the FeIII/FeII ratio in the PB film, resulting in a remarkable enhancement of magnetization accompanied by quasi-reversible electrochromism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...