“Two channel” photocatalytic hydrogen peroxide production using g-C3N4 coated CuO nanorod heterojunction catalysts prepared via a novel molten salt-assisted microwave process
Abstract
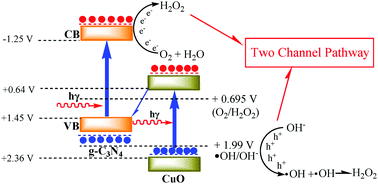
Photocatalytic H2O2 production has gained increasing attention as a sustainable and eco-friendly method to replace conventional anthraquinone-based and electrochemical production processes. In this work, we report a novel molten salt-assisted microwave process to synthesize g-C3N4 coated CuO nanorod heterojunction photocatalysts with outstanding H2O2 production ability. XRD, UV-Vis, N2 adsorption, SEM, TEM, XPS, EIS and PL were used to characterize the obtained catalysts. CN@CuO(4) with the largest heterojunction area displays the highest photocatalytic H2O2 production ability of 6.9 mmol L−1, which is 7.4 and 16.4 times higher than that of individual g-C3N4 and CuO. A “two channel pathway” is proposed for this reaction system which causes the remarkably promoted H2O2 production ability. In addition, compared with a traditional polycondensation method, the catalyst prepared via a molten salt-assisted microwave process exhibits a larger heterojunction area and more effective separation rate, causing higher photocatalytic H2O2 production ability and stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...