pH responsive glycopolymer nanoparticles for targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs†
Abstract
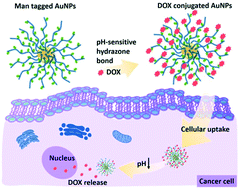
Over the past decade, there has been a great deal of interest in the integration of nanotechnology and carbohydrates. The advances in glyconanotechnology have allowed the creation of different bioactive glyconanostructures for different types of medical applications, especially for drug delivery and release systems. Therefore, the use of more efficient biocompatible nanocarriers with high loading capacity, low overall toxicity and receptor-mediated endocytosis specificity is still in focus for the enhancement of the therapeutic effect. Conjugation of sugar derivatives onto gold nanoparticles presents unique properties that include a wide array of assembling models and size-related electronic, magnetic and optical properties. Here, pH-responsive drug-conjugated glycopolymer-coated gold nanoparticles were prepared by functionalization of gold nanoparticles with thiol-terminated glycopolymers and then subsequent conjugation of doxorubicin (DOX). Among the four different glycopolymers, their drug release, physicochemical characterization (spectroscopy, particle size and surface charge) and in vitro bioapplications with four different cell lines were compared. As a result, pH-sensitive drug delivery via sugar-coated AuNPs was performed thanks to hydrazone linkages between glycopolymers and DOX. Comparative viability tests also demonstrated the efficiency of glycopolymer–DOX conjugates by fluorescence cell imaging. The obtained results reveal that AuNP homoglycopolymer DOX conjugates (P4D) have significant potential, especially in human neuroblastoma cells in comparison to cervical cancer cells and lung cancer cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: MSDE Emerging Investigators 2018


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...