Selective assembly and functionalization of miniaturized redox capacitor inside microdevices for microbial toxin and mammalian cell cytotoxicity analyses
Abstract
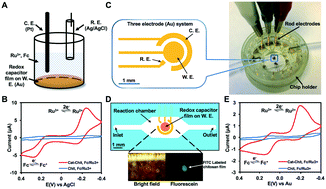
We report a novel strategy for bridging information transfer between electronics and biological systems within microdevices. This strategy relies on our “electrobiofabrication” toolbox that uses electrode-induced signals to assemble biopolymer films at spatially defined sites and then electrochemically “activates” the films for signal processing capabilities. Compared to conventional electrode surface modification approaches, our signal-guided assembly and activation strategy provides on-demand electrode functionalization, and greatly simplifies microfluidic sensor design and fabrication. Specifically, a chitosan film is selectively localized in a microdevice and is covalently modified with phenolic species. The redox active properties of the phenolic species enable the film to transduce molecular to electronic signals (i.e., “molectronic”). The resulting “molectronic” sensors are shown to facilitate the electrochemical analysis in real time of biomolecules, including small molecules and enzymes, to cell-based measurements such as cytotoxicity. We believe this strategy provides an alternative, simple, and promising avenue for connecting electronics to biological systems within microfluidic platforms, and eventually will enrich our abilities to study biology in a variety of contexts.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Lab on a Chip Recent HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
