Electroformation of phospholipid giant unilamellar vesicles in physiological phosphate buffer
Abstract
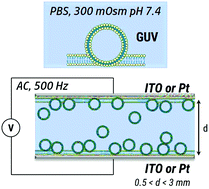
Phospholipid Giant Unilamellar Vesicles (GUVs) are usually prepared by electroformation in water, that is in a low-conductivity solution. We developed a protocol allowing their electroformation in the most common physiological buffer, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). This was achieved based on a specific sequence of increasing electrical fields and for the two usual electrode types for electroformation, namely Indium Tin oxide-coated glass slides and Pt electrodes. These GUVs are stable over time (hour time-scale) and they can be isolated or micro-injected. The membrane composition was modified by adding cholesterol in order to adjust its mechanical properties. The optimal proportion of cholesterol vs. total phospholipid concentration was a ratio of 20 mol%, which increases membrane rigidity and facilitates vesicle microinjection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...