Urinary metabolomic study of the antagonistic effect of P. ginseng in rats with estrogen decline using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Abstract
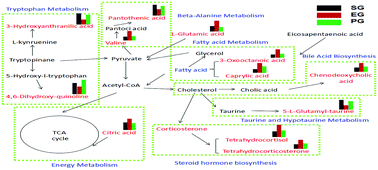
Estrogens are biologically active steroid hormones mainly released from the ovary by ovarian secretion of estrogen into the circulating blood to regulate or function at the distal target. Estrogens play an important role in the central nervous system, cardiovascular system and immune system, especially for post-menopausal women. Panax ginseng Mayer has been reported to relieve women’s menopausal symptoms and affect estrogen activities. However, the mechanism of its estrogen regulation has not yet been clearly investigated. In this work, ovariectomized rats were administered a P. ginseng decoction intragastrically for 8 weeks. Urine samples were analyzed by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) to identify metabolites. The estrous cycle, body weight, uterine weight index and serum hormone levels were measured. The results showed that P. ginseng significantly prolonged the estrus stage, decreased the body weight and serum luteinizing hormone (LH) levels and increased the uterine weight index and serum estradiol (E2) levels of ovariectomized rats. A total of twelve potential biomarkers for which levels changed markedly upon treatment have been identified based on metabolomics. A systematic network analysis of their corresponding pathways indicates that the antagonistic effect of P. ginseng on ovariectomized rats occurs mainly through regulating steroid hormone metabolism, fatty acid biosynthesis, the citric acid cycle and tryptophan metabolism. In conclusion, this study validated the antagonistic effect of P. ginseng in rats with estrogen decline and explored the metabolic and biochemical mechanisms involved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...