Quantifying nanoplastic-bound chemicals accumulated in Daphnia magna with a passive dosing method†
Abstract
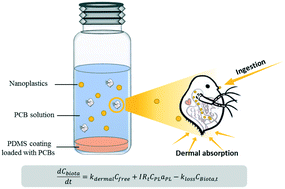
Because of their large surface area and high hydrophobicity, nanoplastics (NPs) possess a large sorption capacity for and strong affinity to hydrophobic organic chemicals, which may substantially alter the environmental behavior, especially the bioaccumulation of hydrophobic organic compounds. The present study aims to examine the effects of nano-size polystyrene (PS) on the bioaccumulation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in Daphnia magna. A novel passive dosing method was developed to quantify the accumulation of NPs in D. magna in different exposure suspensions with various NP concentrations during 2 h and 24 h exposure. Addition of NPs enhanced the amount of PCBs accumulated in D. magna by 1.4–2.6 times compared to no presence of NPs during 24 h exposure. The relative amounts of NP-bound PCBs accumulated in D. magna were 18% to 81% for different PCB congeners at various NP concentrations. The significance of different uptake pathways in the accumulation of PCBs in D. magna with the presence of NPs was found to relate to the chemical properties of PCBs, the ingestion rate of plastics and the exposure conditions. These results have justified additional research efforts toward investigating the fate and toxic effects of NP-bound contaminants ingested by organisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...