Concentrated mixed cation acetate “water-in-salt” solutions as green and low-cost high voltage electrolytes for aqueous batteries†
Abstract
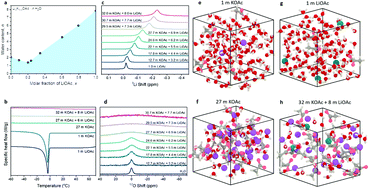
Electrolyte solutions are a key component of energy storage devices that significantly impact capacity, safety, and cost. Recent developments in “water-in-salt” (WIS) aqueous electrolyte research have enabled the demonstration of aqueous Li-ion batteries that operate with capacities and cyclabilities comparable with those of commercial non-aqueous Li-ion batteries. Critically, the use of aqueous electrolyte mitigates safety risks associated with non-aqueous electrolytes. However, the high cost and potential toxicity of imide-based WIS electrolytes limit their practical deployment. In this report, we disclose the efficacy of inexpensive, non-toxic mixed cation electrolyte systems for Li-ion batteries that otherwise provide the same benefits as current WIS electrolytes: extended electrochemical stability window and compatibility with traditional intercalation Li-ion battery electrode materials. We take advantage of the high solubility of potassium acetate to achieve the WIS condition in a eutectic mixture of lithium and potassium acetate with water-to-cation ratio as low as 1.3. Our work suggests an important direction for the practical realization of safe, low-cost, and high-performance aqueous Li-ion batteries.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Energy and Environmental Science HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...