Exploring the scope of capacitance-assisted electrochemical carbon dioxide capture†
Abstract
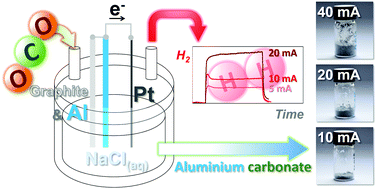
Optimisation of a capacitance-assisted electrochemical carbon-capture process is facilitated by the physical separation of the graphite and aluminium anode electrodes. This facilitates graphite electrode recycling and enables high current and increased aluminium surface area experiments which fix carbon at a higher rate and the same cell-voltage. Quantification of the H2 cathode byproduct shows that this process could be a net energy producer if recycled aluminium is used as the sacrificial anode.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Celebrating our 2019 Prize and Award winners and New Talent: Europe


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...