Recent advances in understanding of the mechanism and control of Li2O2 formation in aprotic Li–O2 batteries†
Abstract
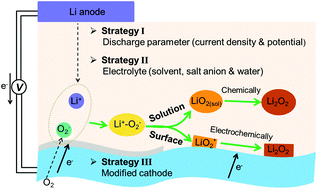
Aprotic Li–O2 batteries represent promising alternative devices for electrical energy storage owing to their extremely high energy densities. Upon discharge, insulating solid Li2O2 forms on cathode surfaces, which is usually governed by two growth models, namely the solution model and the surface model. These Li2O2 growth models can largely determine the battery performances such as the discharge capacity, round-trip efficiency and cycling stability. Understanding the Li2O2 formation mechanism and controlling its growth are essential to fully realize the technological potential of Li–O2 batteries. In this review, we overview the recent advances in understanding the electrochemical and chemical processes that occur during the Li2O2 formation. In the beginning, the oxygen reduction mechanisms, the identification of O2−/LiO2 intermediates, and their influence on the Li2O2 morphology have been discussed. The effects of the discharge current density and potential on the Li2O2 growth model have been subsequently reviewed. Special focus is then given to the prominent strategies, including the electrolyte-mediated strategy and the cathode-catalyst-tailoring strategy, for controlling the Li2O2 growth pathways. Finally, we conclude by discussing the profound implications of controlling Li2O2 formation for further development in Li–O2 batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...