In situ phosphating of Zn-doped bimetallic skeletons as a versatile electrocatalyst for water splitting†
Abstract
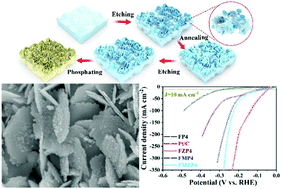
Highly efficient electrocatalysts for water splitting generally involve noble metals (Pt, Ir, Ru, etc.) or expensive transition metals (Ni, Co, Cu, etc.), which have hindered their widespread application. Here, we report a brand-new, low-cost phosphated Zn-doped bimetallic (Fe/Mn) skeleton (Zn-Fe/Mn@Mn-FeP, FMZP4) with genuine potential as a highly effective water-splitting electrocatalyst. Benefiting from heterogeneous atom doping as well as a self-supported electrode composed of a porous Zn-Fe/Mn skeleton and in situ grown phosphides (Mn-FeP) with a hierarchical ultrathin nanosheet structure, which provide rapid electron transport and efficient mass transport channels, the optimized FMZP4 exhibits low overpotentials of 53 mV and 184 mV to reach current densities of 10 mA cm−2 (η10) and 20 mA cm−2 (η20) for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions, respectively, revealing good stability in a long potential cycling test (1000 cycles) and remaining completely stable over an 80 h galvanostatic measurement at 10/50 mA cm−2. More impressively, it needs just 1.79 V to achieve η50 for full water splitting in an alkaline electrolyte and exhibits superior electrochemical durability. The excellent electrocatalytic activity makes it a candidate material for a low-cost electrocatalyst with broad applicability in water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...