Polypropylene separator-reinforced polymer-in-salt solid composite electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries at room temperature†
Abstract
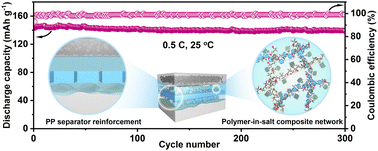
The development of solid-state electrolytes suitable for room-temperature lithium ion batteries is always trapped in irreconcilable contradictions among ionic conductivity, mechanical properties and fabrication complexity. Herein, novel polymer-in-salt sandwich-like solid composite electrolytes (SSCEs) employing a polypropylene separator (PP) as a mechanical reinforcement framework are prepared by a facile two-step coating method. Besides providing affluent free lithium ions, high-content lithium salt dissolved in the poly(vinylidene fluoride) matrix endows maximized amorphous regions and interconnected lithium ion pathways consisting of ionic clusters. Benefiting from the Lewis acid–base interactions introduced by Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12, the polymer crystallinity further decreases and lithium salt dissociates more thoroughly as well. More importantly, the unique PP separator-reinforced structure enables sufficient suppression of lithium dendrite growth by taking advantage of the robust PP framework as an effective physical barrier. Hence, the designed SSCEs deliver significantly improved mechanical properties, high ionic conductivity and a large lithium-ion transference number, enabling high rate performance and excellent cycling stability at room temperature. Besides, the wide applicability of SSCEs is also demonstrated through an assembled LiFePO4/graphite pouch cell operated under various extreme conditions. The results indicate that such polymer-in-salt SSCEs reinforced by a PP separator have a great application prospect in high-performance room-temperature solid-state lithium ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...