Toxic mechanisms of microcystins in mammals
Abstract
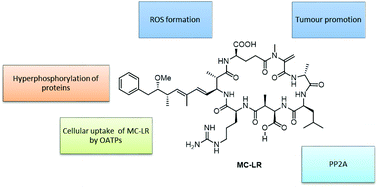
Microcystins, such as microcystin-leucine arginine (MC-LR), are some of the most toxic and prevalent cyanotoxins produced by cyanobacteria in freshwater and saltwater algal blooms worldwide. Acute and chronic exposures to microcystins are primarily known to cause hepatotoxicity; cellular damage and genotoxicity within mammalian livers. However, in vivo studies indicate that similar damage may occur in other mammalian organs and tissues, such as the kidney, heart, reproductive systems, and lungs – particularly following chronic low-dose exposures. Mechanisms of toxicity of mycrocystins are reviewed herein; including cellular uptake, interaction with protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A, cytoskeletal effects, formation of oxidative stress and induction of apoptosis. In general, the mode of action of toxicity by MCs in mammalian organs are similar to those that have been observed in liver tissues. A comprehensive understanding of the toxic mechanisms of microcystins in mammalian tissues and organs will assist in the development of risk assessment approaches to public health protection strategies and the development of robust drinking water policies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Toxicology Research 2017 Most Downloaded Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...